Relative risk is actually the ratio between incidence of outcome/disease among exposed people and that among unexposed people It is usually used in a cohort study where there is a definite population under study and we can calculate incidence rates Hence it is a direct and accurate value compared to odds ratioOdds ratio vs Relative Risk/Hazard Ratio I have a background in physics with a few courses in statistics, but I still have a hard time intuitively understanding OR I get RR as it just is a ratio of probabilities, and I look at HR as RR with a time componentThe relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used for
Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
What is the difference between odds ratio and hazard ratio
What is the difference between odds ratio and hazard ratio-The method of presenting the results of clinical studies can affect their interpretation by clinicians2 and nonclinicians alike3,4 Therefore, it is important to understand the different ways in which results can be presented Absolute risk refers to the simpleUnderstanding Relative Risk, Odds Ratio, and Related Terms As Simple as It Can Get Chittaranjan Andrade, MD ABSTRACT Risk, and related measures of effect size (for categorical outcomes) such as relative risks and odds ratios, are frequently presented in research articles Not all readers know how these statistics




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Increase In Hospital Download Scientific Diagram
Relative risk = 52 103 = 050 Odds of severe exacerbation in Group A = 11/199 (ie a/b) Odds of severe exacerbation in Group B = 22/191 (ie c/d) Odds ratio = 11/199 22/191 = 048 ie (axd) (bxc) To look at the difference between the risk and odds ratio consider the same example (Ventolin vs placebo) but in a group of patients whereJames Pan's answer is accurate and helpful in answering the question, but I would add some additional important characteristics 1 It's never wrong to use Odds ratio (OR), but where you have the true incidence rate it is preferred that you use theIn general If the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference
Definition and derivation Regression models are used to obtain hazard ratios and their confidence intervals The instantaneous hazard rate is the limit of the number of events per unit time divided by the number at risk, as the time interval approaches 0 = → , / ()where N(t) is the number at risk at the beginning of an intervalA hazard is the probability that a patient fails betweenBoth the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds Also odds ratio with odds ratio, relative risk with relative risk, hazard ratio with hazard ratio, can we combine them together?
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a rWhen RR = 1, OR = 1Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio et Risque Relatif dans les études épidémiologiques on retrouve au moins l'un de ces trois indicateurs Skip to content Lundi Vendredi 0900 « Propensity scorebased comparison of the graft failure risk between kidney transplant recipients of standard and expanded criteria donor grafts




Statistics For Gp And The Akt Sept 11




Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller
This is not true for relative risk Switching the rows or columns inverts the odds ratio For example, the odds ratio for no cough given a history of bronchitis = (247/26)/(1002/44) = 0417 = 1/2397 This is the reciprocal of the OR for cough There are only two possible odds ratios, as switching both rows and columns gives If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all If it's above 1, then the tutored group actually had a higher risk of failing than the controls Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the oddsThe ratio between two cumulative incidences (risk in exposed divided by risk in unexposed) gives the relative risk (or risk ratio) While the ratio between two incidence densities (rate in the




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
In the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measuresOdds ratio and relative risk Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome Methods Casecontrol studies are quite common in medical studies Hazard ratio (HR) is nearly the same measure often quoted Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia




Flowchart Of Study Selection Process Hr Hazard Ratios Or Odds Download Scientific Diagram
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeableAn odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I make




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk
The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regret Odds ratio versus Hazard ratio Dos conceptos estadísticos muy usuales en el lenguaje de la Medicina son el concepto de Odds ratio (Ver el tema dedicado a las Medidas de la relación entre variables cualitativas) y el concepto de Hazard ratio (Ver los temas dedicados al Análisis de supervivencia y a la Regresión de Cox )01 = 25This means that those in the control group were 25 times more likely to die than those in the treatment group The relative risk is interpreted in terms of the risk of the group in the numerator How do you interpret incidence risk ratio?




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Nonproportional Hazards For Time To Event Outcomes In Clinical Trials Jacc Review Topic Of The Week Sciencedirect
Variable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) group The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;A rate ratio, ;




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you have data for both groups on theThis implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 × 2 table with an odds ratios of 400 Risk Ratios and Rate Ratios (Relative Risk) Measures of disease frequency can be compared by calculating their ratio Common terms to describe these ratios are Frequently, the term "relative risk" is used to encompass all of these These relative measures give an indication of the "strength of association"



How To Explain The Difference Between Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk To A Layman Quora




Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad
Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RRPute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ; The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds Relative risk is a ratio of two probabilitiesSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
Introduction and background Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratiosA prevalence ratio, or ;An odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I make mention of handwaving;What does a relative risk



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Relative Risk Reduction Can Be Relatively Misleading Youtube
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a studyIf the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio Similarities They will always agree on the direction of comparison In our example above, both will agree that wine consumers have less heart disease than nonconsumers; Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized



1
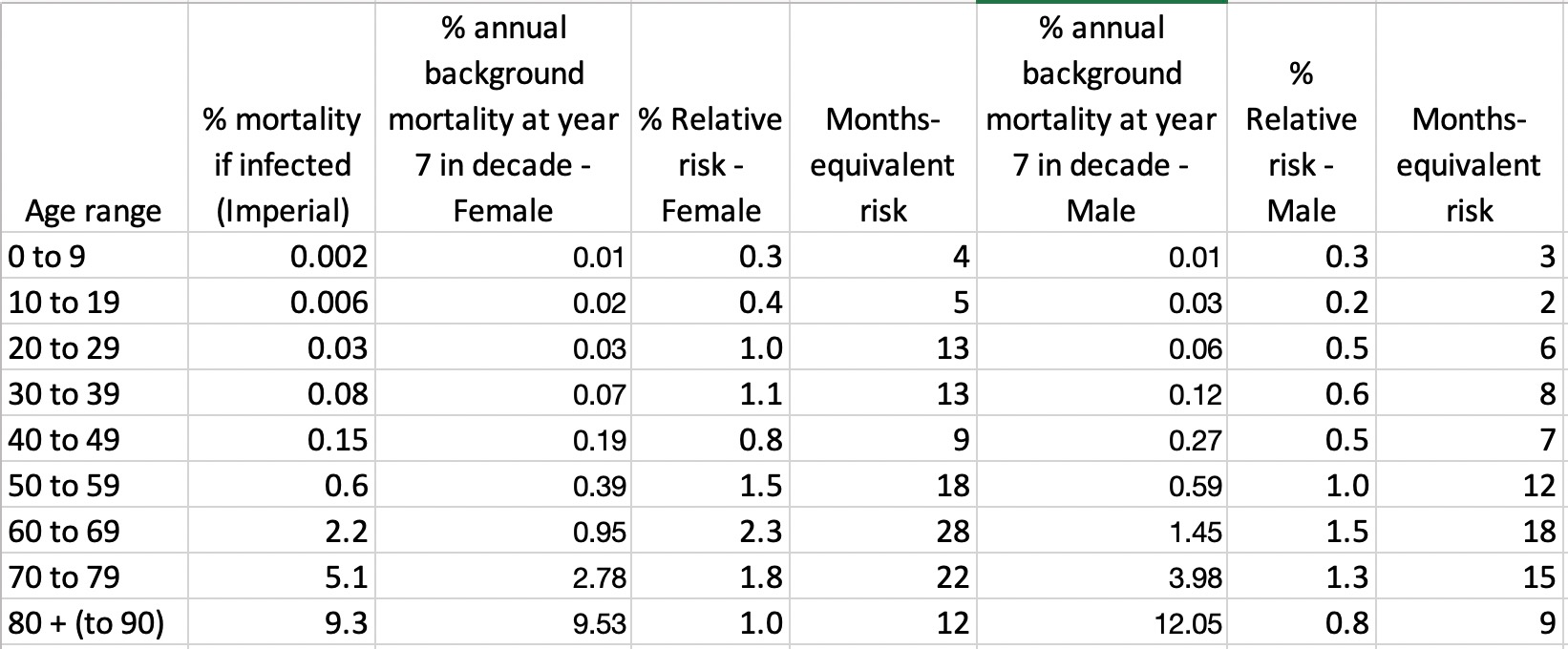



How Much Normal Risk Does Covid Represent By David Spiegelhalter Wintoncentre Medium
There can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ; What does a relative risk of 25 mean? The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk (or odds) between the groups being compared




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
Hazard ratio vs relative risk How to explain the difference between hazard ratio and In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variable For example, in a drug study, the treated population may die at twice the rate per uniHazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk Janez Stare1 Delphine MaucortBoulch2 Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most




Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
In this article, some defining characteristics of the main choices of effect measure risk difference (RD), relative risk (RR), and odds ratio (OR) for binary data are presented and comparedA risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal An example with a control group and a therapy treatment group Treatment group 5 deaths, 95 survive Risk = 5/100 = 005Even an odds ratio;




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% 21 = 058 218 37 223 ÷ 21 = 054 197 37 186 ÷ Table 2 Relation between relative risk, absolute risk and odds ratio 2For multiple logistic regression, and Cox proportional model, each publication may adjust difference factors or confounders, say in the renal failure study, the proteinuria might be the risk factor cause the renal Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 2
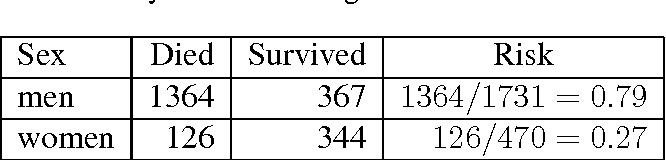



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
What are absolute risks, relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios? This brief communication will clarify the difference between a relative hazard and a relative risk We highlight the importance of this difference, and demonstrate in practical terms that 1 minus the hazard ratio should not be interpreted as a risk reduction in the commonly understood sense of the termIn epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable risk or risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Increase In Hospital Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Part 1 Of 3 Interpreting Odds Risk And Rate Ratio Results With 95 Ci Youtube




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table
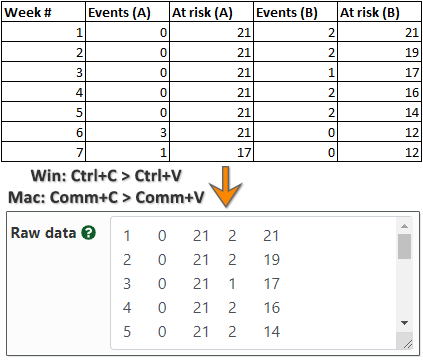



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



1
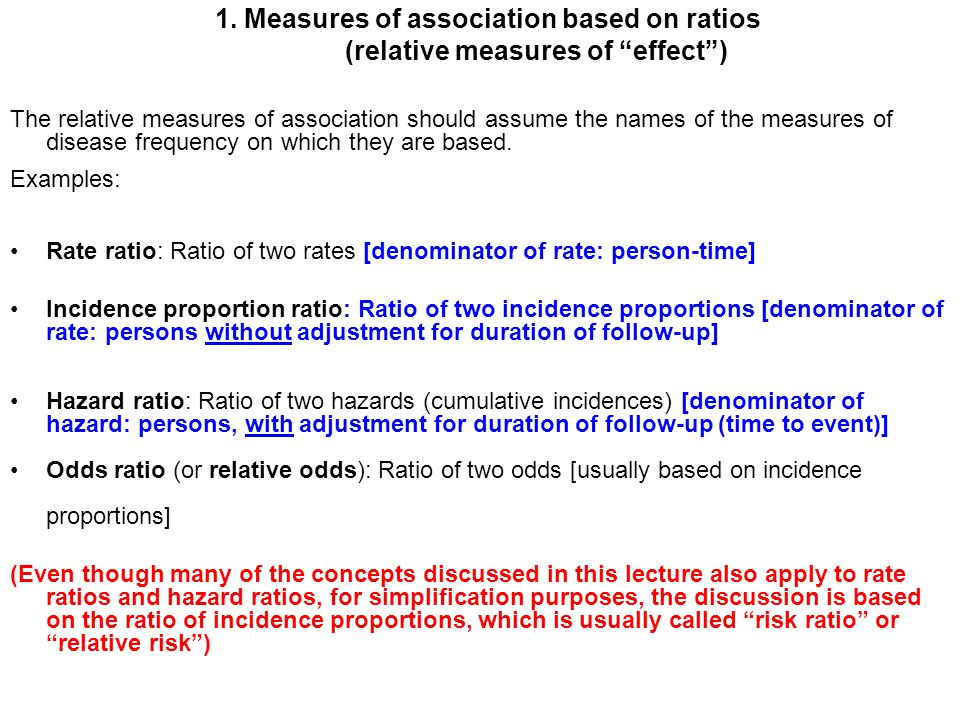



Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Design And Analysis Of Clinical Study Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Dr Tuan V Nguyen Garvan Institute Of Medical Research Sydney Australia Ppt Download



2 Which Of The Following Is Not A Measure Of Relative Risk A B C D E Odds Ratio Risk Ratio Hazard Ratio Number Needed To Treat Rate Ratio Course Hero




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Odds Ratio Article




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Hazard Ratios




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




Lincom Stata




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Hazard Ratio



Wrnmmc Libguides Com Internal Medicine Biostats




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
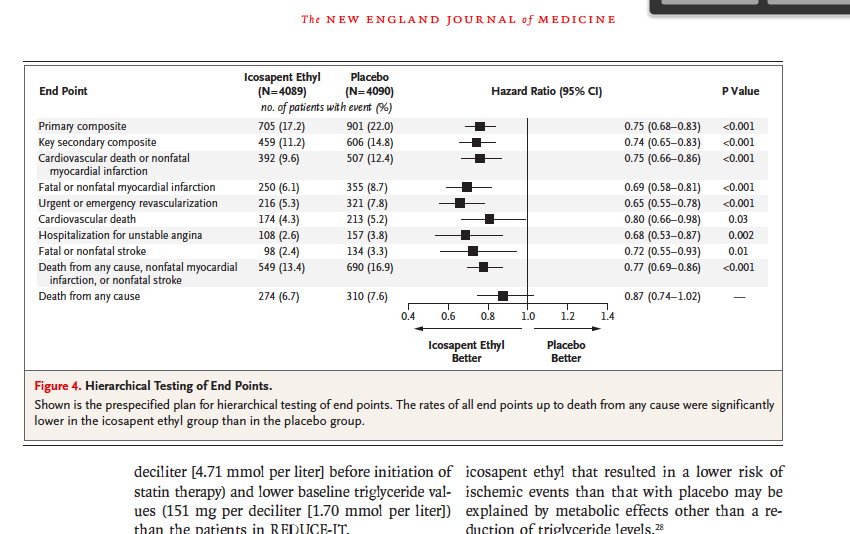



State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Chegg Com




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
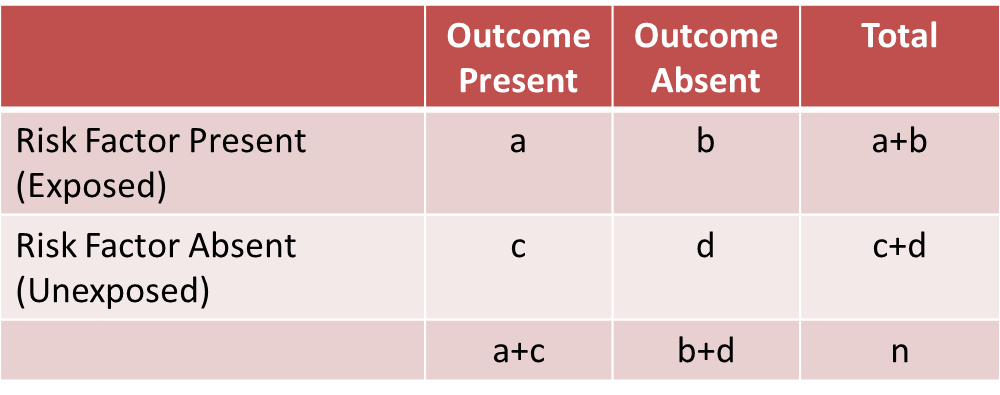



A Stratified Analysis



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
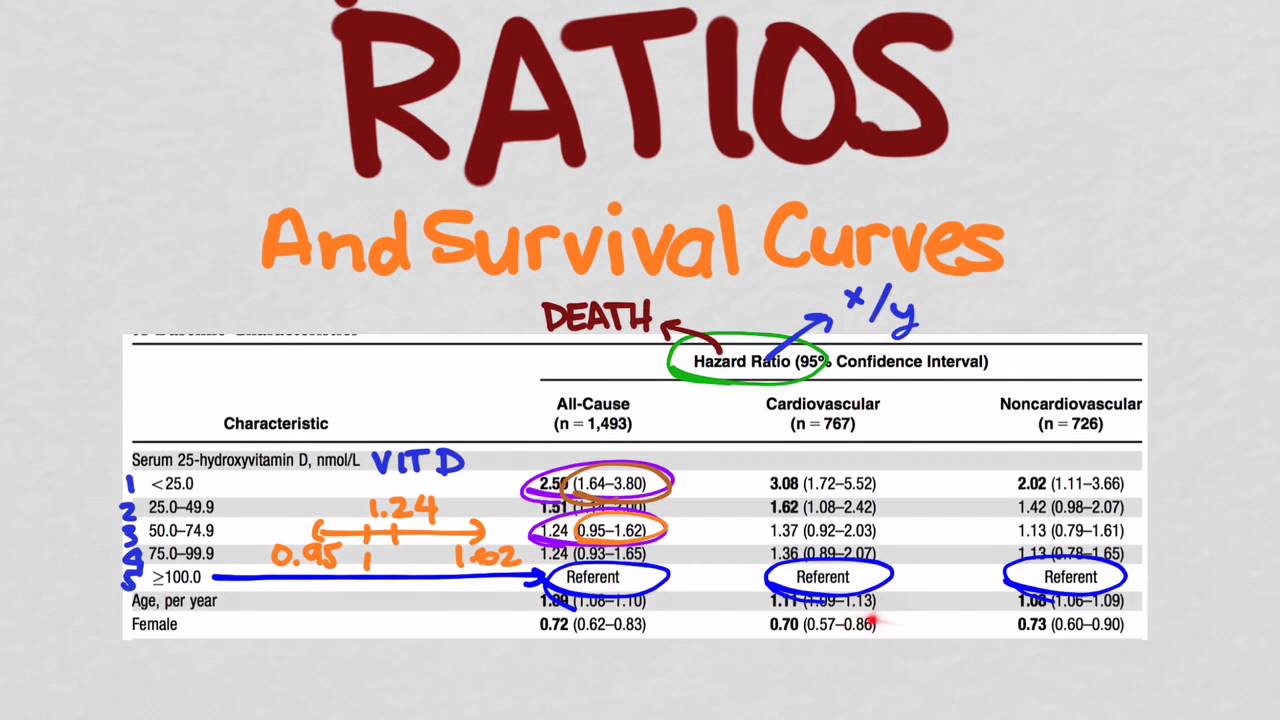



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Epidemiologic And Research Applications In Community Nursing Lecture




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



1




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download
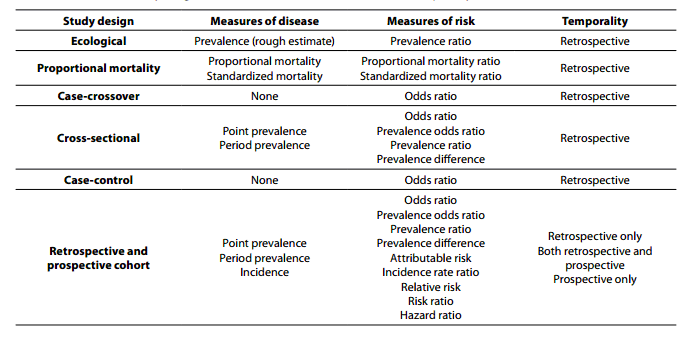



Observational And Interventional Study Design Types An Overview Biochemia Medica




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube
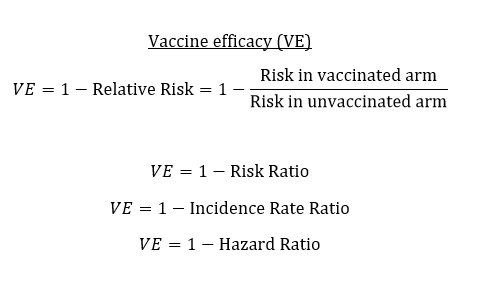



Know The Nuances Of Vaccine Efficacy When Covering Covid 19 Vaccine Trials Association Of Health Care Journalists




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1
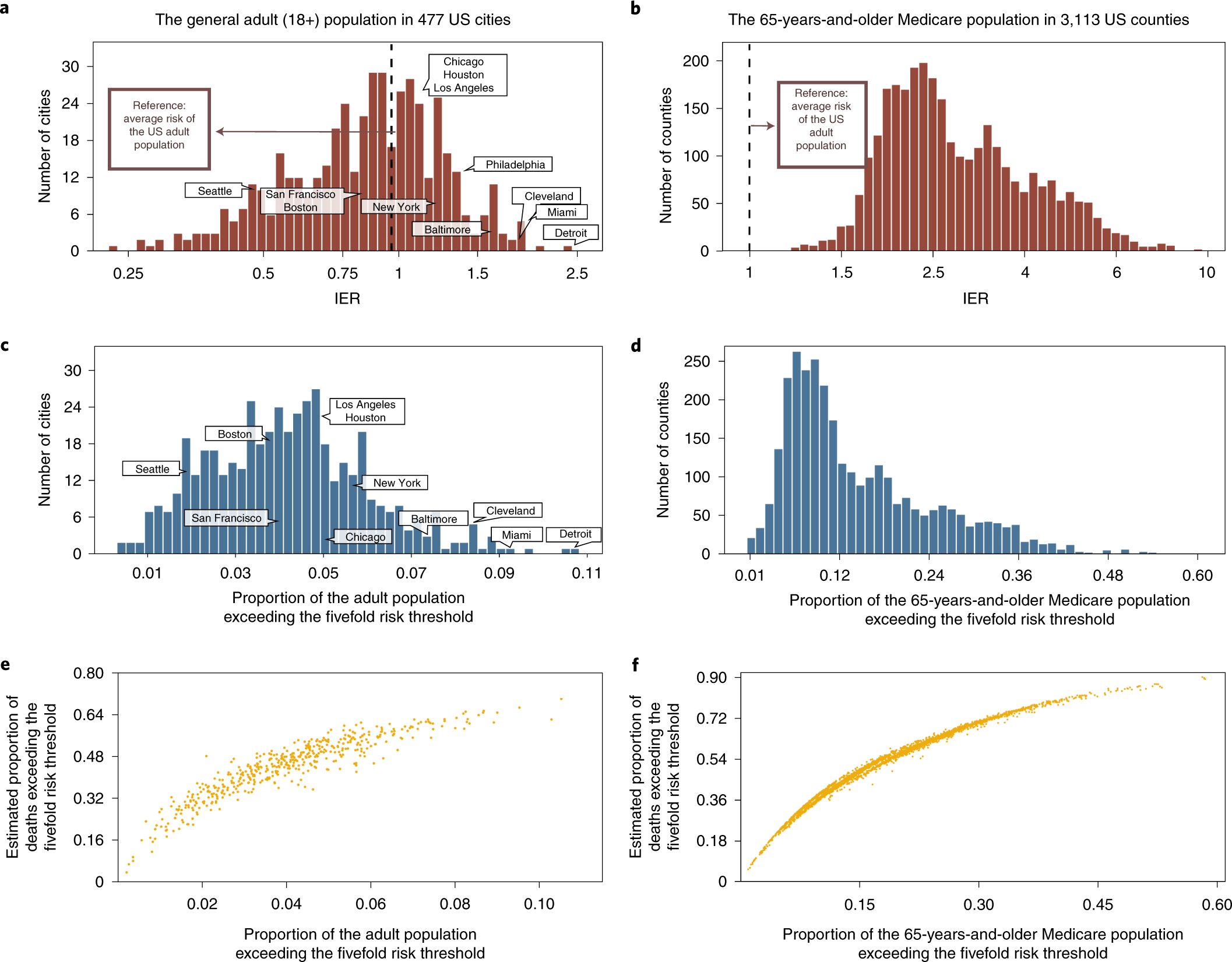



Individual And Community Level Risk For Covid 19 Mortality In The United States Nature Medicine




Challenges In The Design And Interpretation Of Noninferiority Trials Insights From Recent Stent Trials Sciencedirect




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿